Data Center Sustainability – How Renewable Energy is creating an impact

The growing environmental concerns in the last couple of decades have led to a gradual shift from our predominant reliance on conventional energy sources to the new age of green sources. With the pandemic challenging the very fundamentals of our lives, the essence of this green evolution has only gained greater strength, and sustainability has become imperative across all segments.
These unprecedented conditions have led us to become digital-first, driven by the enormous consumption of data around the globe. This will eventually lead to the expansion of data centers in the country as the demand for data grows in the coming decades.
The need to mitigate emissions and manage the transition to carbon-free energy sources has never been more urgent. Data centers consume massive amounts of energy, making them a significant emission source. However, these emissions can be mitigated by adopting renewable energy sources, such as green hydrogen and solar power.
The Need for Sustainable Data Centers
Most of the data is currently being stored in data centers worldwide. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA) estimation, data centers alone will consume approximately 8% of the total energy consumption by 2030. As per the current scenario, data centers consume ~ 1-1.5% of global energy and are responsible for 0.3% of global emissions. Amid all these developments, India isn't untouched. There is a rise in data consumption, and more localized rules and regulations are being implemented in the country.
India's data industry will see a steep rise in data center capacity. As per JLL, the industry has witnessed consistent growth, reaching 636 MW in 2022, and is expected to grow to 1318 MW by 2024. The industry is growing at over 20% annually, leading to a massive rise in scope 1 and scope 2 emissions. Even though renewable energy is one of the low-hanging fruits to reduce the scope 2 emission, there is no significant offtake in certain regions due to complex and unclear policies.
In addition to Scope 2 emission, Scope 1 emission is also significant as the data centers require enormous backup power during any outage to maintain reliability and redundancy. Although large technology companies are aggressively procuring clean energy to operate data center infrastructure through 100% renewable power, the industry uses offset (REC. Green tariff, Carbon Credits, etc.) as a major instrument, which doesn’t help achieve the primary purpose - decarbonization of the grid.
The government is also emphasizing the increased use of renewable energy through different technologies, relaxation in policies and concepts like 24x7 carbon-free energy, easing the development process in open access, and introducing new technologies like green hydrogen. In addition, recently released policies such as Green Energy Open Access Rules 2022, Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Amendment Rules 2022, and The Energy Conservation (Amendment) Bill 2022 are all pushing to offtake more renewable through an easement in policies to drive the sustainability imperative in large energy offtakes like data centers in India.
However, there is still scope for innovation in policy and market mechanisms to transact in clean energy. An integrated policy and solution could be leveraged to push more clean energy in the data center and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) industry to decarbonize operations with new integrated clean technologies, business models, and incentive structures.
AdaniConneX’s Vision for a Sustainable Future
AdaniConneX and EdgeConneX draw inspiration from Adani’s vision of ‘Growth with Goodness,’ a mutual commitment to implementing clean, sustainable, and renewable energy solutions, and a shared goal of becoming minimal carbon-intensive and a business leader that helps enrich lives and contributes to nation building. At AdaniConneX, we will continue building a better India, with "Sustainability" integral to our business model. It's about the lives we touch, the communities we nourish, and the innovations leading to a sustainable future.
In line with these beliefs, we express our commitment to Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles and leverage the diversity and size of our business to create sustained and scalable impact. With the philosophy of growth with goodness, we intend to positively impact people and the planet to enable the digital economy.
Leveraging Renewable Energy for Operational Net Zero Data Centers by 2030
Under the sustainability commitment, AdaniConneX strives to achieve 100% renewable usage and become an operational net zero data center by 2030. Our focus areas are on the following initiatives across our portfolio -
- AdaniConneX will set up decarbonization targets, periodically monitor energy consumption patterns, and identify areas where renewable energy sources can be explored.
- We will explore the integration of renewable technologies to increase renewable energy penetration (without certificates) from the commencement of operations.
- Going further, we will source renewable energy to reduce the carbon footprints associated with energy sourcing from utility companies. Under this, we shall work closely with the ecosystem, i.e., developers, technology providers, etc., to explore solar, wind, battery storage, and pump-hydro storage energy technology to increase renewable energy penetration and ensure the supply of 24x7 carbon-free energy.
- Engagement with stakeholders, government, and developers in policy enablement to ease the accessibility of renewables procurement.
Enabling 24x7 Carbon-free Energy to Achieve India’s Climate Goals
Standalone renewables have intermittency issues, which don't solve the purpose of eliminating the emission to a greater extent, posing a challenge to decarbonization. Moreover, though regional uncertainty and the availability of renewable resources are evident, most of the next-generation technologies are still too costly for large-scale development.
At AdaniConneX, we are promoting 24x7 carbon-free energy in the region. The integrated combination of solar, wind, battery storage, and pump-hydro energy storage could deliver dispatchable and reliable clean energy. This can also help mitigate the variability associated with intermittent sources, i.e., solar and wind.
The declining cost of solar and wind (solar power plunged over 80% since 2010) should be utilized to integrate battery storage and pump-hydro energy storage, which can act as a constant clean power generation source and potentially solve the intermittency issues, ultimately decarbonizing the grid. This will eliminate carbon emissions and help reduce the cost of balancing the grid. The aim is to eliminate carbon emissions from the grid and decarbonize energy procurement. As per Central Electricity Authority (CEA), the Indian grid is currently close to 10-12% carbon-free and is expected to rise by 25-30% by 2030. So, 24x7 carbon-free energy would play a crucial role in decarbonizing the grid and helping India achieve its climate goals.
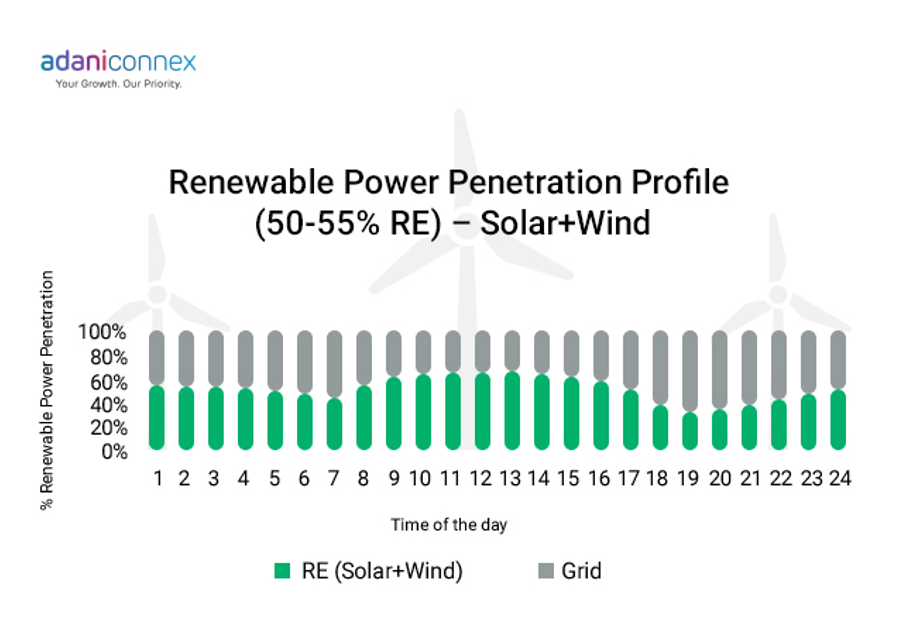

For example, based on our assumption, a typical 100 MW data center could eliminate approximately 8.28-10 MtCO2 carbon emission from Scope 2 by using 24x7 carbon-free energy and potentially save significant money (including carbon tax + direct savings through energy arbitrage) considering 15 years of tenure.
Although as a hybrid renewable energy or a standalone entity, 24x7 carbon-free energy would not be cost-competitive. Therefore, a development roadmap is required by integrating various low-carbon technologies like battery storage and pump-hydro at different stages of development by 2030 or earlier to make it cost-competitive.
Prioritizing Renewable Energy Procurement for Data Centers
The need to prioritize renewable energy procurement for the data center industry is imminent. Data centers and ICT companies can develop their captives or source renewable power from third-party developers under a long-term contract arrangement. As new renewable power procurement models evolve globally, ICT companies can also look into VPPAs or Green Tariff options depending upon their intent to decarbonize their physical infrastructure.
AdaniConneX is also prioritizing the interstate transmission system for a renewable energy project to be developed for data centers, as they will start commencement within 2-3 years from the day of implementation. This will pace up the renewable energy investment in the region. Additionally, the data centers ready for service are primarily firm, so there is more clarity on when the demand will hit and start consuming a large amount of energy. Finally, the waiver of Inter-State Transmission system (ISTS) charges will also pace renewable development growth, and consumers must leverage these benefits to maximum potential.
Leveraging Green Hydrogen as a Backup Option
Hydrogen is already a critical industrial feedstock. Unlike other energy options and associated emissions, green hydrogen should also be explored to reduce the Scope 1 emission. Primarily, in data centers, Scope 1 emission is generated when the DG operates during the startup, backup operations, and other routine maintenance if required. Compared to Scope 2, Scope 1 emission is very minimal. However, if we count every drop of water, it leads to achieving a bigger purpose. These DG systems contribute the majority of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) from backup energy.
Green hydrogen use-case in a data center
The declining cost of green hydrogen driven by low-cost renewable power, the plunging price of electrolyzer and mass production, and technological improvements in the electrolyzer can make green hydrogen an alternative option for backup power.
Recently, AdaniConneX did a pilot techno-commercial study of 3 MW to integrate the fuel cell in our data center facility at Chennai 1 Data Center. It has given the line of sight to evaluate the low-carbon technologies in our operations, which have a fast dynamic response, longer life, silent operation, and zero local emission.
To drive the sustainability initiative, AdaniConneX is ready to leverage the Adani group’s experience in large-scale renewable energy deployment and efficient integration of new-generation renewable technologies to provide the decarbonizing solution to data center customers. Our ability to deploy large-scale Renewable Energy can create a win-win situation for potential customers to decarbonize their data storage/process. There is a need for industry collaborative actions to drive the long-term sustainability agenda and achieve the decarbonization goal.
Related Blogs
